Plant in general requires these 16 essential elements for proper growth and development at various stages of its growth cycle. These 16 elements are:
- Carbon
- Hydrogen
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorus
- Potassium
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Sulphur
- Boron
- Chlorine
- Copper
- Iron
- Manganese
- Molybdenum
- Zinc
Other than these 16 essential elements plant also requires Cobalt, Iodine, Selenium and Sodium but they does not require them from external sources and they are not essential for plant growth, development and survival.
These nutrients are classified into three groups on the basis of nutrient quantity required.
1. Basic Nutrients: They are Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen and are generally available to plants from air, water and soil. They constitute 96% of the total dry matter of the plant.
Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen are both basic and macro nutrients that are not needed to applied externally.
Macro nutrients are further classified into two categories i.e. Primary nutrients and Secondary nutrients.
A. Primary Nutrients: They are Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P) and Potassium (K). They are required in specific fixed and proper ratio by a plant to grow and develop very well.
B. Secondary Nutrients: They are Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), and Sulphur (S). They are also required in large quantity but lesser than primary nutrients.
3. Micro Nutrients: They are Manganese (Mn), Iron ( Fe), Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), Boron (B), Molybdenum ( Mo), and Chlorine (Cl). They are required in very less amount i.e. why they are also known as minor or trace elements.
These 16 elements that are required in larger and lesser amount have their specific roles in plant growth and development.
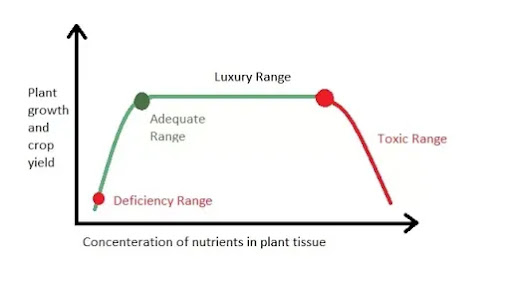
From various research on nutrients uptake and response in plants it has been found that after a certain level of application of plant nutrient causes toxicity in plants. Excessive application of nutrients can even kill your plants.
The Graph you are viewing represents the toxicity of nutrients in plants. Adequate range represents the point where nutrients are available in appropriate and required amount for growth and development.
Luxury range represents the excess amount of nutrients that doesn’t affects the growth and development of the plant and the toxic range represents the excess amount of nutrients present in plant tissue that can cause toxicity.
I have seen many new farmers and gardeners committing this mistake of applying excess amount of fertilizers. Later on these excess nutrients harm plants and decreases overall productivity.
With the advancements and availability in digital media many people who have not even studied about agriculture and plants have started spreading so many misconceptions.
Newbie farmers as well as gardeners should follow only trusted You tube channels and websites that provide scientific and clear information. Following the wrong platform can prove to be harmful in future.
I have studied agriculture and I try to provide you only those content that are valid and are scientifically proven. I follow Dr.B.N. Viswanath (Father of Organic Terrace Garden, India), ICAR, GBPAU, SDSUV, etc.
They are certified, valuable, trusted and respected organisation in the field of Agriculture. There are people on digital platform that are sharing valuable and correct information, you can follow them too to make your plants healthy and happy.
Toxicity Symptoms of Nutrients in Plants
Research has shown that when a high concentration of fertilizer salts are present in soil solution then it causes chlorosis and necrosis of the leaf margins in several plants.
Higher levels of nitrogen increases susceptibility to bacterial and other diseases. If the concentration of ammonium ions increases then it can affect the uptake of calcium.
Higher levels of Calcium and Potassium can affect the uptake of magnesium in plants from the root region. In poinsettia it was found that higher levels of calcium in foliar region caused reduction in total bract area i.e. leaf.
All micro nutrients if applied in excess amount can harm your plant. When iron and manganese are applied in higher amounts they cause necrosis and chlorosis in leaves.
Boron toxicity also causes lesions on leaves of the plant. Copper toxicity causes reddish brown lesions on the leaves of the plant. They are the common symptoms of toxicity, you must have noticed them in your plants and thought that it is because of deficiency but the truth is different.
So do not waste your time and money on applying excess amount of fertilizers. Check from the trusted sources about the fertilizer requirements of particular plant that you are going to grow and apply according to the need of your plant.