Drought is one of the most significant environmental challenges that farmers & agricultural producers face. The effects of drought on agriculture are far-reaching and can lead to crop failure, reduced yields, and economic losses. Drought conditions cause a lack of moisture in the soil, which can result in poor plant growth and reduced crop yields.
It can also lead to the drying up of water resources such as rivers, streams, and ponds, which are essential for crop irrigation. Therefore, it is very important to undersand what is draught, its causes and steps required to overcome losses.
Table of Contents
What Is Drought?
Drought is a meteorological phenomenon that occurs when there is a deficient supply of moisture in a region due to sub-normal, infrequent distribution of rainfall, higher water requirement, or a combination of these factors. The definition of drought varies among experts, with some early workers describing it as a prolonged period without rainfall.
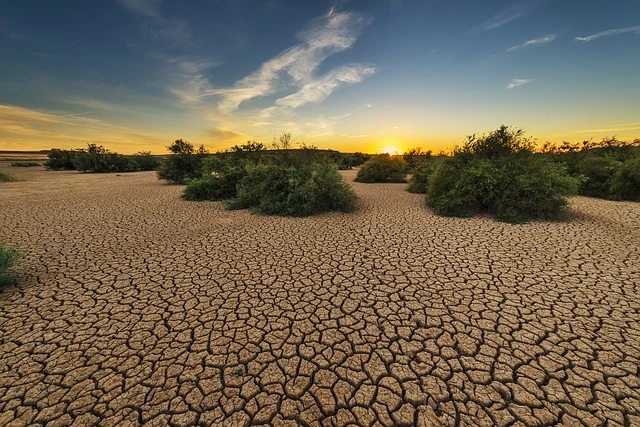

When there is a prolonged deficiency of soil moisture, it can lead to agricultural drought, which adversely affects crop growth. This happens when there is an imbalance between soil moisture & evapotranspiration needs of an area over a fairly long period of time, causing damage to standing crops and reducing yields.
Classification Of Drought
Droughts can be categorized as meteorological drought, hydrological drought and agricultural drought.
- Meteorological drought: It is characterized by a prolonged period of below-normal precipitation levels in a particular area. When the amount of rainfall received in a season is less than 25% of its long-term average value, it is considered a meteorological drought.
The severity of the drought is further classified as moderate if the rainfall deficit ranges between 26 to 50 percent & severe if it exceeds 50 percent of the normal value.
- Hydrological drought: It refers to a scarcity of surface and sub-surface water supplies that leads to a shortage of water for normal & specific needs. This can happen even during times of above-average precipitation if water usage increases and diminishes the reserves.
- Agricultural drought: It is typically triggered by meteorological & hydrological droughts and occurs when there is insufficient soil moisture and rainfall during the crop period. Plant water demand depends on various factors such as weather conditions, the type of crop, growth stage, and soil properties.
Agricultural drought occurs when crops are vulnerable during different stages of growth, from emergence to maturity. If there is 4 consequetive weeks of severe draught having rainfall scarcity of more than 50% of the long term average or weekly rainfall of 5 centimetres or less from mid-May to mid-October when 80% of the total crop is planted, then it is classified as agricultural draught in India.
You will also love reading them,
READ MORE: WHAT IS SOIL EROSION & CAUSES?
READ MORE: EFFICIENT IRRIGATION SYSTEMS!
Types Of Agricultural Drought
Crop production in rainfed regions is often affected by various types of drought, including early season, mid-season, late-season, and chronic drought.
- Early season drought: It can happen due to either delayed onset of monsoon or prolonged dry spells soon after the onset. This can lead to seedling mortality, poor crop stand, and seedling growth, which may require re-sowing.
- Mid-season drought: It occurs when there is a lack of soil moisture availability between two successive rainfall events during crop growth. Its effect varies depending on the crop growth stage, duration, and intensity of the drought spell.
- Late-season or terminal drought: It is caused by early cessation of monsoon activity, mainly during years with late commencement or weak monsoons. Terminal drought is critical as the crop yield strongly depends on water availability during the reproductive stage.
- Chronic drought: It is common in arid regions where rainfall and stored soil moisture are inadequate to meet crop water requirements for most of the year. The growing period is typically limited to 6 to 7 weeks, and such areas are characterized as highly drought-prone.
Other types of droughts are:
- Apparent Drought: In low to medium rainfall areas, mismatching of cropping pattern according to moisture availability causes apparent drought.
- Contingent Drought: In humid & sub-humid climates, abnormal failure of rainfall or infrequent rainfall causes contigent draught. It only affects a small area.
- Invisible Drought: It can occur ven in areas with normal rainfall frequency but inadequate to meet the evapotranspiration losses. It causes reduced crop yield.
Causes Of Drought
- Climate Change: It is the most significant contributor to the increase in occurrences worldwide. The increase in global temperatures has led to more frequent and severe droughts in many regions of the world. According to NASA, global surface temperatures have risen by about 1 degree Celsius since the late 19th century.
- Deforestation: It is another significant cause of this phenomenon. Trees play a crucial role in maintaining the water cycle by regulating the amount of water released into the atmosphere through transpiration. When trees are cut down, the amount of moisture in the soil decreases, leading to a reduction in rainfall.
In addition, deforestation contributes to global warming by releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, further exacerbating drought conditions. According to the World Wildlife Fund, around 18 million acres of forest are lost every year, equivalent to 27 to 30 soccer fields per minute.
- Overuse of Water Resources: Human activities, such as agriculture, industry, and urbanization, require vast amounts of water, which can lead to depletion of water resources. According to the World Bank, over 80% of the world’s population lives in areas where water security is a concern.
- Natural Variability: Natural variability is a natural cause of drought, resulting from changes in the earth’s atmospheric circulation patterns. These changes can lead to periods of reduced rainfall, leading to drought conditions.
The El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a natural climate cycle that can cause drought in some parts of the world. During an El Nino event, the sea surface temperature in the equatorial Pacific Ocean rises, leading to a reduction in rainfall in parts of Asia and Africa.