The 7 steps of farming are plowing, sowing, manuring, irrigation, weeding, harvesting and storage. Farming begins with preparing the field by plowing to create an ideal seedbed for the germination of seeds. Then seeds are sown and manures are applied to provide adequate nutrients to the growing plants.
Irrigation plays a crucial role in thermoregulation and supplying essential nutrients to plant parts from the soil. Weeding is necessary to remove unwanted plants that can hinder the growth of the main crop in the field. Timely harvesting plays a crucial role in getting quality harvest & storage helps in extending the shelf life of the harvested produce.
Table of Contents
7 Steps Of Farming With Picture
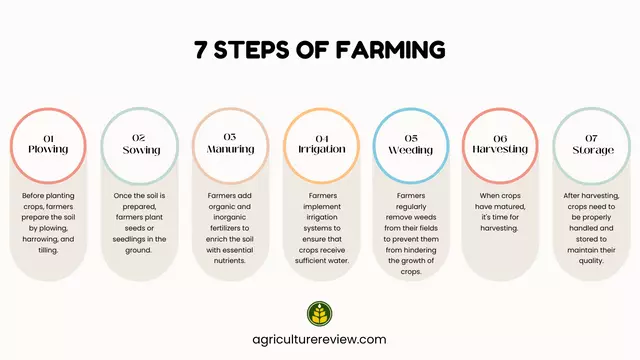
Here are the 7 steps of farming in detail.
Plowing
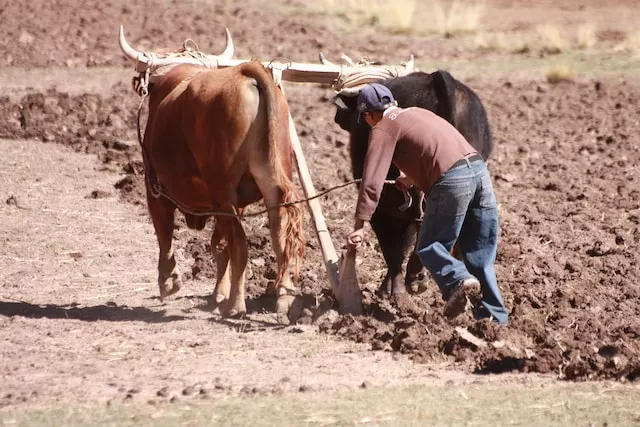

Plowing is the practice of disturbing the upper layer of the soil with the help of a plow for creating ideal seed bed for sowing of seeds and facilitating good growth in plants. It involves loosening of soil as well as removal of weeds.
Sowing

Sowing is the process of planting seeds in the ground or soil to grow crops. Seeds are placed in the soil at a specific depth and spacing to ensure that they get adequate aeration, moisture, temperature and nutrients for successful germination and growth of the plant.
Manuring

Manuring also known as fertilizing in agriculture is a process of adding organic or inorganic substances to soil to improve its fertility and provide essential nutrients to plants. It is essential for nutrients to optimum yield and maintain soil fertility. Nutrients can be supplied to plants by using manure which is organic or by using inorganic fertilizers which are made from chemicals or minerals.
Irrigation

Irrigation is the artificial application of water to the soil. Water is applied before sowing, after sowing and during plant growth period. It helps in ensuring consistent water supply to the plants, increase productivity, counter the effects of droughts, improve the quality of crops, control erosion, etc.
Weeding

Weeding is the process of removing unwanted or undesirable plants from the field. These unwanted plants compete for nutrients, water and sunlight with the main crop. If they are left in the field, then can reduce crop yield drastically. Therefore, weeding is an essential task because it helps the desired crop to grow more effectively by reducing competition for resources.
Harvesting

Harvesting refers to the process of gathering mature crops from fields, orchards, or vineyards. It is typically done when the crops are at their peak maturity stage, however, crops such as vegetables, sprouts, field crops as silage, etc. can be harvested before physiological maturity.
Harvesting methods vary based on the type of crop. For example, grains such as wheat and rice are harvested using specialized machinery like combine harvesters.
Storage

Storing harvested produce is crucial to maintain their quality and prevent spoilage. Crops like grains, pulses, and oilseeds are stored in dry conditions to prevent moisture-related issues, while fruits, vegetables, and flowers require cold storage to maintain their freshness.






How a farmer grow different kinds of crops in the field and write the complete procedure with diagram and picture paste.
Hi,
This article has been written for educational purposes for agriculture students. The article is about common steps of farming with attributed images and not about the cultivation practices of a single crop. Kindly read carefully!